Company Analysis: Apple Inc. (AAPL) – Understanding the Cupertino Giant, its Ecosystem, and Future Prospects
Table of contents
Introduction: More Than Just Devices – The Empire of Apple Inc.
When we talk about Apple, our minds immediately go to iPhones, Macs, or iPads, products that have redefined entire sectors and have become global status symbols. But behind the iconic bitten apple logo, there’s much more than just devices: there’s Apple Inc. (AAPL), a true technological and cultural ecosystem, as well as one of the world’s most valuable and influential companies.
This comprehensive Apple stock analysis aims to clarify who Apple Inc. is, how it was born, what it does through its vast portfolio of products and services, and what its strategic directions and ambitions for the future are. Understanding Apple shares and its corporate strategy is essential for anyone wanting to invest in a company that not only dictates trends but profoundly influences how we live and interact with technology.
Who is Apple Inc. and its Shares? A Giant of Innovation and Value
Apple Inc. is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California. Founded on principles of innovative design, ease of use, and unprecedented hardware-software integration, it has grown to become the most recognized brand and, for long periods, the company with the highest market capitalization globally.
It is a prominent member of the “Big Five” US tech companies (along with Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft) and a pillar of the Nasdaq. Its shares are traded on the Nasdaq under the ticker AAPL, and are among the most beloved and held by retail and institutional investors worldwide. Although the company has a broad shareholder base, the influence of its management and corporate culture, shaped by its founders, remains a key factor in its identity and success.
When Was it Born? A Story of Genius, Crisis, and Rebirth
Apple’s history is an odyssey of innovation, near-failures, and spectacular rebirths:
- Birth and Early Successes (1976-1985): Apple Computer Company was founded on April 1, 1976, by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne. The introduction of the Apple II (1977) and the Macintosh (1984) marked the company’s initial successes and entry into the personal computer sector, with an emphasis on intuitive graphical interfaces.
- Period of Difficulty and Jobs’ Return (1985-1997): After Steve Jobs’ departure in 1985, Apple went through turbulent years, struggling to innovate and maintain market share. Jobs’ return in 1997, with the acquisition of NeXT, marked the beginning of its rebirth.
- The Era of Iconic Products and the Mobile Revolution (1998-2011): Under Jobs’ leadership, Apple launched a series of revolutionary products: the iMac (1998), the iPod (2001), the iTunes Store (2003), the iPhone (2007), and the iPad (2010). These products not only saved the company but propelled it into the tech pantheon, redefining mobile computing and the music industry.
- The Tim Cook Era and the Growth of Services (2011-Today): After Steve Jobs’ passing in 2011, Tim Cook took the helm. The company consolidated the iPhone’s success, expanded its product line (Apple Watch, AirPods), and strategically shifted focus towards the Services segment, which became an increasingly important growth driver for Apple shares.
What Does Apple Inc. Do? The Perfectly Integrated Ecosystem
Apple operates through an integrated ecosystem of hardware, software, and services, which is at the heart of the value of its shares:
- Products (Hardware): This is the most recognizable segment and the primary source of revenue, although its incidence on total revenue is decreasing in favor of services. It includes:
- iPhone: The most popular smartphone globally, the core of the ecosystem.
- Mac: The line of desktop and laptop computers (MacBook, iMac, Mac mini, Mac Studio, Mac Pro).
- iPad: The line of tablets.
- Wearables, Home and Accessories: Includes Apple Watch, AirPods, Apple TV, HomePod, and a wide range of accessories.
- Services: This segment is growing exponentially and represents an increasingly stable and profitable source of income. It includes:
- App Store: The app distribution platform.
- Apple Music: Music streaming service.
- iCloud: Cloud storage service.
- Apple Pay: Mobile payment platform.
- Apple TV+: Video streaming service with original content.
- Apple Arcade: Subscription gaming service.
- Apple News+, Apple Fitness+, Apple Card, and much more.
- User loyalty to the Apple ecosystem ensures a recurring revenue stream from these services, a key factor for the stability of Apple shares.
- Software (Operating Systems):
- iOS (for iPhone), iPadOS (for iPad), macOS (for Mac), watchOS (for Apple Watch), tvOS (for Apple TV), and visionOS (for Apple Vision Pro). The tight integration between hardware and software is a unique Apple strength.
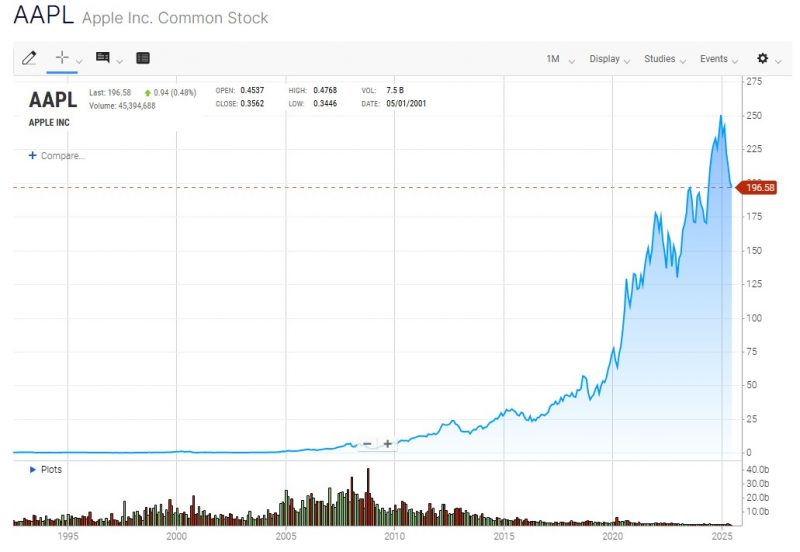
Historical Data and Apple Stock Performance: An Essential Part of Your Apple Stock Analysis
Understand the history of Apple shares in this Apple stock analysis is fundamental to assessing their resilience and potential.
- Apple IPO (1980): Apple went public on December 12, 1980, with an Initial Public Offering (IPO) price of $22 per share. It was an immediate success, raising more capital than any other IPO since Ford Motor Company.
- Exponential Growth and Stock Splits: Since its listing, and particularly since the beginning of the 21st century, Apple has demonstrated extraordinary revenue and earnings growth. To make shares more accessible, Apple has carried out several stock splits:
- 2-for-1: May 1987, June 2000, February 2005
- 7-for-1: June 2014
- 4-for-1: August 2020
- These splits multiplied the number of shares held by investors, reducing the price per share and increasing liquidity, without altering the overall value of the investment.
- Dividends and Buybacks: Apple began paying a dividend in 1987 (later suspended and reinstated in 2012) and has implemented massive share repurchase programs (buybacks). These capital return policies are a strong signal of financial solidity and an incentive for those evaluating Apple shares.
Simulation of Potential Investor Gain (Hypothetical Example):
To illustrate value growth, let’s consider a purely indicative example:
- Hypothetical Scenario: Imagine an investor purchased 1 Apple share at the IPO price of $22 on December 12, 1980.
- After all Stock Splits: That single original share would have transformed into an incredible number of shares: 1 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 7 * 4 = 224 shares.
- Current Value (hypothetical): If we consider a share price of approximately $210 (hypothetical value in mid-June 2025, post-split), the total value of those 224 shares would be approximately $47,040 (224 shares * $210/share).
- Capital Gain: Compared to the initial investment of $22, the capital gain would have been $47,018.
- Percentage Return: This equates to a return exceeding 213,700% on the initial capital in just over 44 years, not counting distributed dividends.
This example highlights Apple’s extraordinary ability to generate long-term value for its shareholders, transforming a small investment into significant capital. It is essential to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.
Apple stock analysis : Things that are not always easy to find (and why they are important for those investing in Apple Shares)
- Brand Strength and Customer Loyalty: Apple enjoys brand loyalty and pricing power almost unparalleled. The closed ecosystem creates a “lock-in” for customers, making it difficult to switch to competing platforms. This translates into consistent sales and recurring service revenues.
- Supply Chain Management: Apple’s ability to manage its complex global supply chain, ensuring the production of millions of high-quality devices at low costs, is a huge and often underestimated competitive advantage.
- The Growth of Services: Although the iPhone remains the dominant product, Apple’s Services segment is the true driver of margin growth and revenue stability. Monitoring subscriber growth and the expansion of these offerings is crucial for valuing Apple shares.
- Enormous Cash Reserves: Apple holds one of the largest cash reserves among public companies. This liquidity offers flexibility for strategic acquisitions, research and development investments, and generous capital return programs to shareholders.
Risks (Important Considerations):
- Regulatory and Antitrust Risk: Apple faces increasing scrutiny from regulatory authorities and governments worldwide, particularly regarding App Store practices, its dominant position in mobile, and antitrust issues. These risks can lead to significant fines and changes to the business model.
- Constant Innovation and the “Next Big Thing”: Apple’s ability to innovate and launch revolutionary products has historically been its strength. The pressure to find the “next big thing” and keep pace with technological evolution is a continuous challenge.
Apple stock analysis : What Does Apple Want to Do in the Future? Vision and Strategic Directions for the Shares
Apple is a company in constant evolution, with a clear strategic vision to sustain growth and strengthen its dominant position, influencing the value of its shares:
- Expansion of the Services Segment: Apple will continue to invest heavily in the development and expansion of its services, introducing new offerings and increasing the subscriber base. This is its highest-margin growth engine.
- New Product Categories: The introduction of Apple Vision Pro marks Apple’s entry into the “spatial computing” market. The company aims to further develop this technology and explore other emerging categories (e.g., health, advanced home automation, long-term autonomous vehicles).
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Apple is integrating AI more deeply into its products and services (Siri, computational photography, etc.). Investments in AI will continue to grow to improve user experience and maintain competitiveness.
- Growth in Emerging Markets: Apple is expanding its presence in key markets like India and Southeast Asia, where the growing middle class and increasing disposable income offer immense opportunities for iPhone sales and ecosystem expansion.
- Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: Apple is a leader in sustainability commitments, aiming for carbon-neutral products and a closed-loop supply chain. This is not only ethically responsible but also strengthens the brand image and attracts investors focused on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria.
- Health and Wellness: With the Apple Watch and its advanced sensors, Apple is becoming a significant player in the health and wellness sector, with the potential to transform personal monitoring and prevention.
Conclusion of our Apple stock analysis : Investing in Apple Shares – A Giant with a Unique Ecosystem
Apple Inc. is not just a device manufacturer; it is an ecosystem builder, a branding master, and a financial giant. For an investor, understanding its deep integration between hardware, software, and services, its unparalleled customer loyalty, its financial solidity, and its constant forward-looking vision, is crucial for making an informed decision about Apple shares. Despite regulatory challenges and iPhone dependence, its capacity for innovation, impeccable management, and growing emphasis on services make Apple a company with still remarkable growth and stability potential in the global technology landscape.